A sternotomy and clamshell incisions were performed and methylene blue dye is seen outside the pleura and distributed in the paravertebral gutters advertisement content uploaded by andrew sawka.
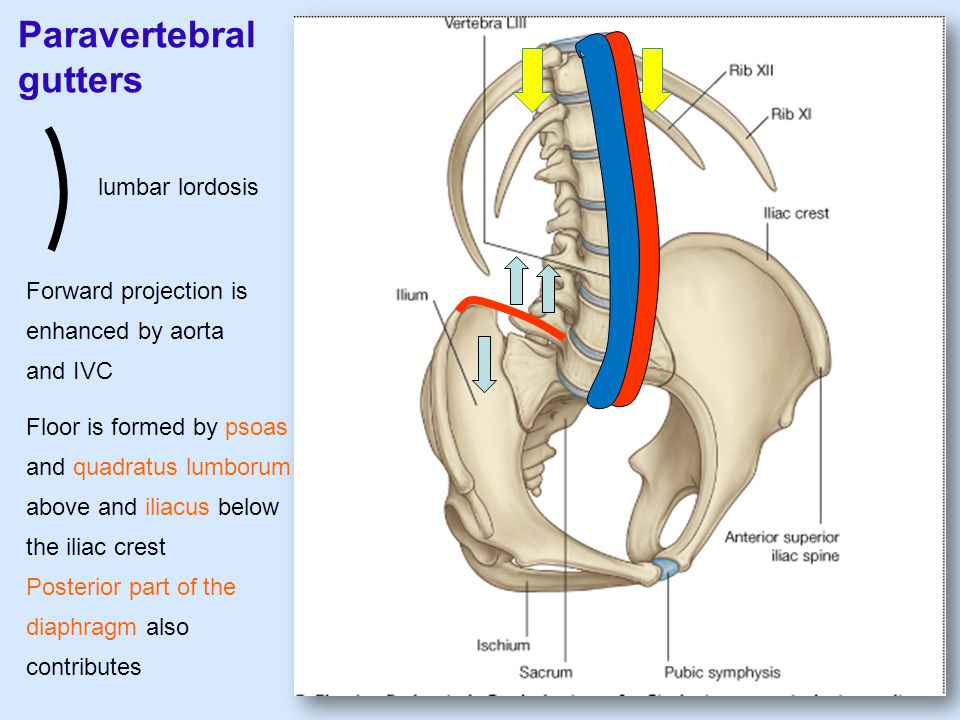
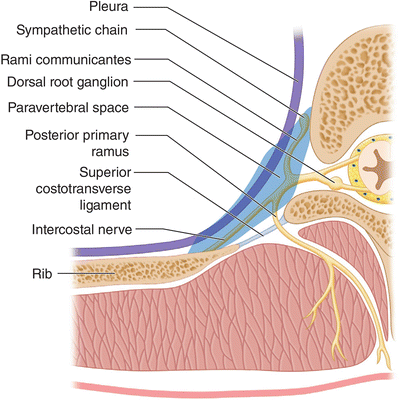
Contents of paravertebral gutter.
A slight right anterior oblique rao when performing lateral chest x rays superimposes the posterior ribs as they are aligned to the divergent beam.
Relations on each side the suprarenal gland sits like a cap on the superior pole of the kidney.
The prevertebral space is a space in the neck.
On one side it is bounded by the prevertebral fascia.
As the kidneys lie in the paravertebral gutter the renal hilum faces forwards as well as medially while its long axis runs obliquely parallel to the lateral border of psoas major.
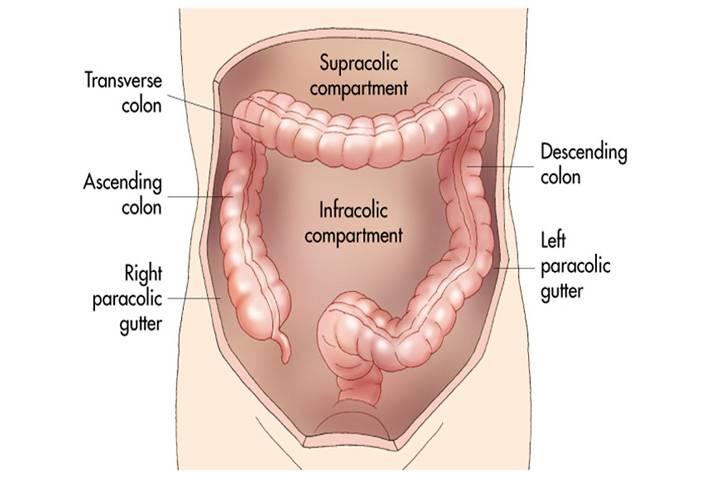
These gutters are clinically important because they allow a passage for infectious fluids from different compartments of the abdomen.
Psoas major is a triangular bilaterally paired muscle that forms part of the floor of the paravertebral gutter.
Often radiographers will place their thumbs on the patient s scapulae and place the patient into.
The gutter part refers to the inside.
Fluid from an infected appendix can track up the right paracolic gutter to the hepatorenal recess.
Paravertebral space superior inferior within the paravertebral gutter.
The gutters are rounded outward on the patient s back.
In the thorax across the heads necks of ribs medial through the intervertebral foramen epidural anesthesia lateral contribution to cervical stellate ganglion brachial plexus intercostal lumbar plexus blockade anterior not possible unless pleura breached.
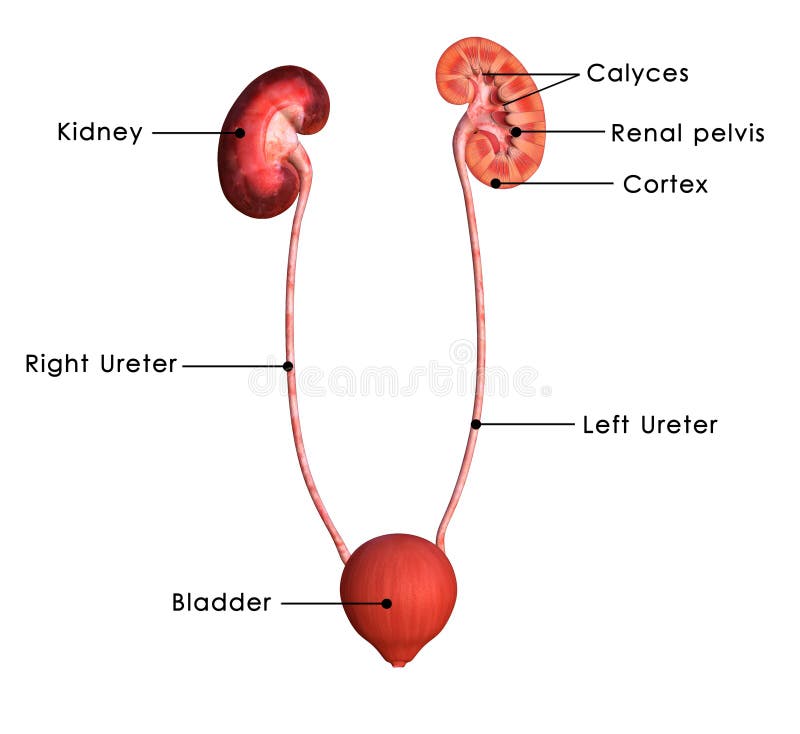
Kidneys lie in the paravertebral gutters at the level of t12 to l3 vertebrae moves about 3cm in vertical direction during movement of diaphragm ureter runs inferiorly from each kidney lies in a mass of perirenal fat posterior to peritoneum on the posterior abdominal wall 35.
It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliopsoas muscle the strongest hip flexor of the human body.
The patavertebral gutters are the rounded expanse of ribs formed when the back parts of the ribs curve from the outside edges towards the spinal column.
Clinical significance bile pus or blood released from viscera anywhere along its length may run.
It includes the prevertebral muscles longus colli and longus capitis vertebral artery vertebral vein scalene muscles phrenic nerve and part of the brachial.